Table of Contents
Which mushrooms are best for ADHD?
Benefits of Lion’s Mane on Brain Function: A Comprehensive Guide to Benefits, Dosage, and Nutrition
In today’s blog post, we’re diving into a challenging question: Can Lion’s Mane help with ADHD? In the clinic where I work, a staggering 90% of our clients battle not just ADHD, but a spectrum of learning disabilities including autism, challenging behaviors, and concentration issues, among others. Despite medication and emotional support, many struggle because their brains simply don’t cooperate, making therapy sessions less effective.
A large majority of adolescents have a poor sleep hygiene as well, feeling tired.
The anti fatigue activities observed in the polysaccharides extract of Hericium erinaceus
These polysaccharides are known to possess various physiological activities such as antitumour, antioxidant, antiviral activities; immunomodulatory, antiinflammatory and anticarcinogenic actions (Rathore et al., 20171).
Let’s explore the potential of Lion’s Mane together!
Lion’s mane mushrooms, long celebrated for their medicinal health benefits, especially in boosting neurological health, have recently captured the Western world’s attention. Known as nature’s brain booster, this remarkable mushroom is making waves as a natural supplement for enhancing memory and overall neurological function.
While the specific query relates to Attention Deficit Hyperactivity Disorder (ADHD), the provided research papers do not directly address this condition. However, they do offer insights into the neurological and psychological effects of Lion’s mane mushrooms, which may be tangentially relevant to ADHD through their impact on cognitive function and mood disorders.
As a natural remedy, it has gained attention for its possible positive effects on brain health, with research suggesting it may support cognitive function, memory, and mental clarity. For individuals with ADHD, the question often arises whether Lion’s mane can provide symptomatic relief or improve cognitive capabilities. Scientific research into its efficacy is ongoing, with some studies indicating that daily consumption of lion’s mane could be beneficial.
Let’s start with some statistics regarding ADHD from Digital NHS UK
Between 2017-18 and 2021-22, the percentage of patients with a learning disability and diagnosed with ADHD increased from 5.5% to 8.0%, while the proportion of those without a learning disability but diagnosed with ADHD rose slightly from 0.5% to 0.8%.
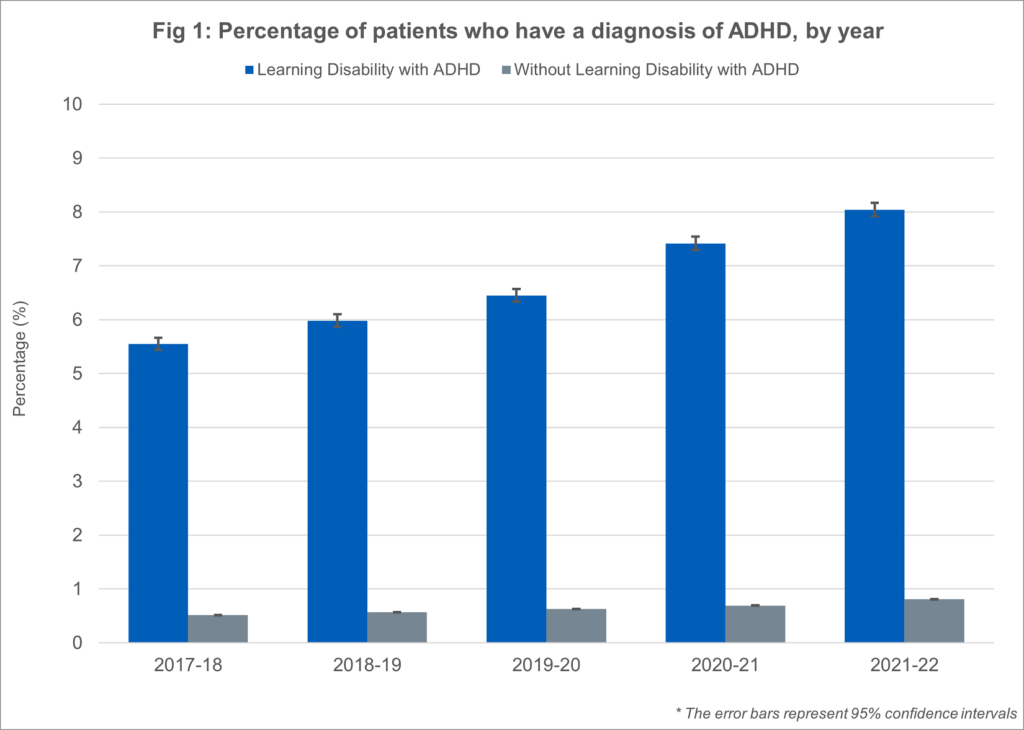
A recent study published in BJPsych Open analyzed data from 7 million individuals aged three to 99, sourced from the UK primary care database IQVIA Medical Research Data (2000-2018). Of the participants, 35,877 had ADHD diagnoses, and 18,518 received ADHD medication prescriptions. While the overall number of individuals on ADHD medication remains relatively low, the study revealed a higher prevalence of ADHD diagnoses in children compared to adults, particularly in boys and men.
The increase in ADHD diagnoses and medication prescriptions was most pronounced in boys aged 10-16, with rates rising from 1.4% and 0.6% in 2000 to 3.5% and 2.4% in 2018, respectively.
What country has the highest rate of ADHD?
Australia leads in ADHD prevalence among its total population at 3.72%, while the US has the highest rate among children and teens at 8.1%.
How is ADHD in the US compared to other countries?
The US has the highest global ADHD rate among children and adolescents at 8.1%.
ADHD Symptoms
Symptoms of ADHD include impulsiveness, disorganization, poor time management skills, difficulty focusing, and restlessness. ADHD symptoms start in childhood but are increasingly recognized to persist in adults.
The symptoms of ADHD can have a significant impact on daily life. Inattention can lead to difficulties with completing tasks, forgetfulness, and poor time management. Hyperactivity can lead to restlessness, fidgeting, and difficulty sitting still. Impulsivity can lead to interrupting others, speaking out of turn, and taking risks without considering the consequences.
These symptoms can impact academic, social, and occupational functioning. Children with ADHD may struggle in school and have difficulty making and keeping friends. Adults with ADHD may have difficulty with time management, organization, and maintaining employment.
While there are medications and behavioral therapies available to manage ADHD symptoms1 , some individuals are looking for alternative treatments to supplement or replace traditional approaches.
Lion’s Mane Mushrooms
Lion’s mane mushroom (Hericium erinaceus) has many common names: bear’s head mushroom, bearded hedgehog mushroom, bearded tooth fungus/mushroom, hog head fungus, Hou Tou Gu (Chinese), monkey head mushroom, old man’s beard mushroom, Pom Pom Mushroom, Satyr’s beard fungus, white beard mushroom and Yamabushitake (Japanese)
It is an edible fungus, which has a long history of usage both culinary and medicinal uses in China, India, Japan, and Korea. It is known for its cascading white spines that resemble a lion’s mane, hence its name. Lion’s Mane is a nutritional powerhouse, containing protein, fiber, and various vitamins and minerals.
This mushroom is rich in bioactive important components, especially β-glucan polysaccharides, which are responsible for anti-cancer, immuno-modulating, hypolipidemic, antioxidant, and neuro-protective activities of this mushroom, promoting digestion as well. H. erinaceus has also been reported to have anti-microbial, anti-hypertensive, anti-diabetic, and wound healing properties among other therapeutic potentials.
Nutritional value of Lion’s Mane mushrooms
Lion’s Mane is a functional food, valued not only for its flavor but also for its nutritional content. Notably, it is rich in antioxidants which contribute to overall health and wellness. The mushroom provides a source of bioactive compounds that can support cognitive function and potentially aid in the management of ADHD symptoms.
Here is a breakdown of the nutritional value of Lion’s Mane Mushroom per 100 grams:
Calories: 375 calories and 6.69 g moisture
| Protein | 20.46 grams |
| Fat | 5.06 g |
| saturated fat | 0.76 g |
| polyunsaturated fat | 0.83 g |
| total unsaturated fat | 1.85 g |
| Carbohydrates: | 61.80 g |
| Dietary Fiber | 39.20 grams |
| vitamin B1 | 0.16 mg |
| B2 (riboflavin) | 2.26 mg |
| B5 (pantothenic acid) | 7.40 mg |
| Vitamin D | 57 IU |
| Calcium | 8 mg |
| Copper | 1.66 mg |
| Iron | 6mg |
| Niacin (B3) | 11.80 mg |
| Selenium | 0.091 mg |
| Potassium | 2.7 g |
| Sodium | 4 mg |
Other Compounds:
- Polysaccharides (beta-glucans)
- Hericenones and erinacines (support nerve growth)
Overall, Lion’s Mane Mushroom is a nutritious food that can be easily incorporated into a healthy diet. Due to its lobster or shrimp flavor, it is often used as a meat alternative in soups
Potential Benefits of Lion’s Mane on Brain Function
Lion’s mane mushrooms medical research suggests Hericenones and erinacines compounds can stimulate the production of nerve growth factors, which may improve memory, enhance focus, and facilitate learning.
Does Lion’s Mane improve cognition?
One of the key ways that Lion’s Mane may support brain function is through its ability to stimulate the production of neurotrophic factors, which are proteins that promote the growth and survival of neurons. According to a study published in the National Library of Medicine, Lion’s Mane mushroom contains compounds that can stimulate the production of nerve growth factor (NGF) and brain-derived neurotrophic factor (BDNF), two of the most important neurotrophic factors in the brain.
NGF and BDNF are critical for the growth and survival of brain cells, and they play a key role in the formation of new neural connections. By promoting the production of these factors, Lion’s Mane mushroom may help to protect against cognitive decline and support overall brain health.
In addition to its potential benefits on nerve growth, Lion’s Mane mushroom has also been shown to have cognitive-enhancing properties. According to this study Lion’s Mane mushroom contains Erinacines that can support the production of neurotransmitters, which are chemicals that transmit signals between neurons in the brain. Furthermore, research suggests that Lion’s mane mushroom can have a positive impact on mental health conditions such as anxiety and depression.
Can Lion’s mane help with ADHD? Lion’s mane ADHD study
Lion’s Mane Benefits ADHD. Impacts on Attention and Hyperactivity
According to Verywell Health, Hericium erinaceus has been found to potentially benefit those with ADHD, as they might help in alleviating symptoms of inattention and hyperactivity, and play a role in improving focus and concentration in individuals with ADHD—an area where traditional stimulant medications like Adderall are typically prescribed. Early investigations suggest that Lion’s Mane’s influence on neurotransmitters could moderate attention and reduce hyperactivity, although it is important to note that clinical evidence is not yet definitive.
Lions Mane and Adderall
While stimulant medications are a standard treatment for ADHD, they are not without side effects, which can include sleep disruption, appetite suppression, and increased heart rate. In contrast, Lion’s Mane is being studied as an alternative treatment that might offer benefits for ADHD with a lower risk of adverse effects.
Support for Neurodevelopmental Disorder Management
ADHD, as a neurodevelopmental disorder, encompasses challenges with executive functioning and behavioral regulation. Lion’s Mane is thought to support brain health and could potentially promote the management of ADHD. Evidence pointing to its role in the growth and repair of nerve cells suggests it could have longer-term neurodevelopmental benefits for children and adults when used alongside behavioral therapy and other management strategies.
Can You Take Lion’s Mane Every Day?
The optimal dosage of Lion’s Mane mushrooms varies depending on the form of the supplement, whether it’s in powder, extract, or capsule form. Clinical trials investigating Lion’s Mane have used various dosages, with some studies administering up to 3 grams per day without adverse effects. Users are advised to follow the manufacturer’s recommendations on the supplement label, as these are typically based on standardized extracts. Lion’s Mane mushroom is also available in powder form, which can be added to smoothies or other beverages.
Potential Side Effects and Allergies
Lion’s Mane is considered safe for most people, and studies have rarely reported side effects. However, as with any supplement, individual reactions can occur, including gastrointestinal discomfort. It’s also important to consider the risks associated with its use, especially for those with mushroom allergies. In terms of impact on heart rate, blood pressure, or breathing, no significant evidence suggests Lion’s Mane has adverse effects on these parameters. Nevertheless, users should monitor their body’s responses and consult a healthcare provider with concerns.
You might wonder how long it takes for mushroom supplements to work?
Based on client feedback, mushroom supplements can start working quite quickly. Many people report feeling more energy, clarity, and focus within just a few hours of their first cup. For those dealing with anxiety or panic attacks, noticeable improvements can often occur within 24-48 hours. Pain management benefits have been observed in less than 12 hours, while improvements in bowel movements and skin health typically happen within 5 days. The Elixir of Life, which contains 7 powerful mushrooms with 30% beta-glucan and no additives, seems to work very fast for Elixir Of Life users.
Frequently Asked Questions
How does Lion’s Mane mushroom affect brain function?
Lion’s Mane mushroom contains compounds that stimulate NGF production, which can enhance neuronal growth and synaptic plasticity. This means that Lion’s Mane mushroom can improve communication between brain cells, leading to enhanced memory, focus, and overall cognitive function.
What is the recommended daily dosage of Lion’s Mane for cognitive enhancement?
There is no standard recommended dosage for Lion’s Mane mushroom supplements. However, most studies have used doses ranging from 500 to 3000 mg per day, divided into two or three doses. It is important to follow the dosage instructions on the product label and consult with a healthcare professional before consuming Lion’s Mane mushroom supplements.
Does Lion’s Mane mushroom have any interactions with medications?
There is limited research on the potential interactions between Lion’s Mane mushroom and medications. However, it is important to consult with a healthcare professional before consuming Lion’s Mane mushroom supplements, especially if you are taking any medications or have a medical condition
Key Takeaways
- Lion’s mane mushrooms offer cognitive and mental health benefits.
- There’s growing interest in its potential as a natural remedy for ADHD
- Lion’s Mane mushroom has been used for centuries in traditional Chinese medicine for its potential health benefits.
- Lion’s Mane is a nutritional powerhouse, containing protein, fiber, and various vitamins and minerals.
Start your journey to a healthier you today!
Elixir of Life with 30 % Beta Glucan is GMO-free, sustainable, and of the highest quality, so you can trust that you’re getting the best possible product for your brain and gut health needs.
Don’t wait any longer to start your journey towards a healthier, happier gut – try Mushroom Elixir Of Life today!
Conclusion
Lion’s Mane contains bioactive compounds such as erinacines and hericenones therefore has been recognized for its medicinal values and potential to enhance cognitive function, protect against brain cell death, and improve mental clarity.
It’s suggested that individuals with ADHD might find Lion’s Mane beneficial due to its properties that support mental clarity and overall cognitive performance. Moreover, its nutritional profile provides a variety of health benefits that can be harnessed through daily consumption.
The interest in Lion’s Mane’s influence on the brain’s function has led to many considering it as a complementary approach to managing ADHD symptoms. Its role in improving memory and supporting mood is supported by various anecdotal reports and preliminary research. To maximize the effects of Lion’s Mane, one could integrate it with other natural methods for a holistic approach to ADHD symptom management.
In essence, Lion’s Mane has emerged as a natural supplement with properties that could potentially benefit those with ADHD. Its integration into one’s diet should be done with consideration of individual health circumstances and in consultation with a healthcare provider.
Reference
1 What is ADHD?. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. Accessed 5/1/2023.
- Rathore, H., Prasad, S., and Sharma, S. (2017). Mushroom nutraceuticals for improved nutrition and
better human health: A review. PharmaNutrition 5, 35-46 ↩︎



[…] erinaceus, also known as Lion’s Mane, is a culinary and medicinal mushroom with a distinctive appearance. Traditionally recognized in […]
[…] Lion’s mane is another popular choice, often discussed in the context of menopause, as it may aid in managing symptoms without directly influencing estrogen levels. Turkey tail and Cordyceps mushrooms are also associated with supporting hormonal health during menopause, with cordyceps offering additional potential benefits for energy levels and vitality. […]
[…] improve memory and learning abilities in experimental models, suggesting their potential as nootropic agents1 […]
[…] pot ajuta ciupercile (Lion’s Mane) — mecanisme […]