Table of Contents
Recently I was asked what is the best vitamin for Carpal Tunnel syndrome and which is better: vitamin B6 or B12 for carpal tunnel syndrome.
I had the opportunity to work with Outpatients: plastic surgery Guys and St Thomas NHF Through my experience, I’ve encountered numerous individuals grappling with Carpal Tunnel Syndrome (CTS), many of whom were navigating the recovery process post-surgery. Some faced the challenge of undergoing multiple surgeries, often with outcomes that fell short of expectations. It’s a reminder of our mission to empower and support everyone on their journey toward wellness, advocating for informed decisions that lead to better health outcomes.
The diagnosis relies on clinical symptoms, neurologic exams, and EMG tests. Risk factors for CTS include being female, pregnant, obese, repetitive wrist movements, job-related factors, and chronic conditions like diabetes, thyroid issues, acromegaly, and connective tissue disorders.1
Warning! Surgery is typically reserved for severe cases involving significant strength and sensitivity loss, altered electromyography, or thenar hypotrophy.
Pharmacological treatments include either local steroid infiltrations or systemic administration of corticosteroids or non-steroidal antiinflammatory drugs (NSAIDs), especially when synovitis is present; these drugs are needed to reduce the inflammation of the compressed nerve, although recent meta-analyses have not confirmed the efficacy of NSAID
Non-surgical treatments for Carpal Tunnel Syndrome (CTS) include splinting, exercises, yoga, therapeutic ultrasound, ergonomic adjustments, and oral medications or vitamins. Due to varied outcomes and inadequately controlled trials, the efficacy of their use in managing CTS remains uncertain.2
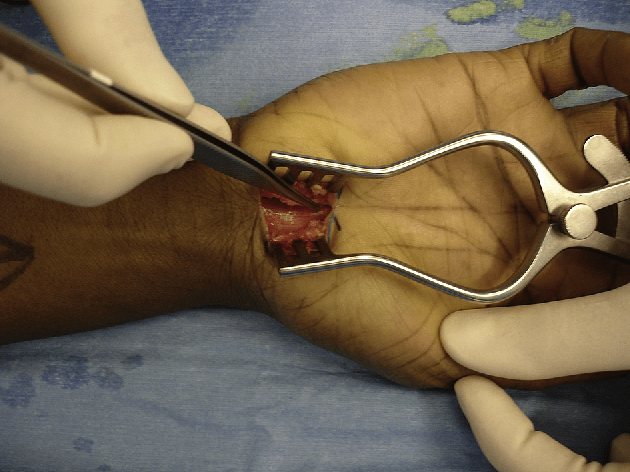
Carpal tunnel release surgery. (Reproduced by kind permission of Mr R. Ragoowansi MB, MSc, FRCS (Plast), Consultant Plastic, Aesthetic and Hand Surgeon, Barts Health NHS Trust).
Conditions associated with carpal tunnel syndrome
Carpal tunnel syndrome (CTS) is the most prevalent focal mononeuropathy, constituting 90% of all neuropathy cases.
CTS is a condition that can cause pain, numbness, and tingling in the hand and arm. The condition occurs when one of the major nerves in the hand — the median nerve — is squeezed or compressed as it travels through the wrist. In the search for non-surgical treatment options, various studies have explored
Who is most likely to get carpal tunnel syndrome
Carpal tunnel syndrome mainly affects women, with a male-to-female ratio of 1:3, and typically presents in individuals aged 40 to 60, often within two years of symptom onset.
The prevalence of Carpal Tunnel Syndrome (CTS) in the general population varies between 1% and 5%. CTS exhibits a higher incidence among females compared to males, manifesting a 3:1 female-to-male ratio. Furthermore, the likelihood of developing CTS is notably increased in individuals who are obese, with the risk being doubled.

For those considering vitamin supplements, dosage is an important consideration, especially since intake recommendations can vary. For instance, some specialists recommend vitamin B6 for alleviating CTS symptoms.
Vitamin B6 (pyridoxine) supplementation has been associated with significant improvement in clinical symptoms and electrodiagnostic results in patients with CTS, suggesting its potential as a conservative treatment option.
Vitamin B6 is generally safe under 200 mg daily, though monitoring for symptom changes is advised, especially with high doses over long periods
There is debate among researchers and healthcare providers as to whether vitamin B6 or B12 is more effective in managing symptoms of Carpal Tunnel Syndrome.
Meanwhile, the long-term effects of untreated Carpal Tunnel Syndrome can be serious, including persistent weakness and loss of hand function. While the link between CTS and heart disease is not direct, conditions typically associated with heart disease like diabetes and obesity can increase the risk of developing CTS.
Key Takeaways
- Vitamin B6 supplementation has been associated with significant improvement in clinical symptoms and electrodiagnostic results in patients with CTS, suggesting its potential as a conservative treatment option
- A controlled dosage of vitamin B6 (100 mg b.i.d.) has been reported to provide satisfactory improvement in 68 percent of patients treated conservatively for CTS
- Vitamin D supplementation has been linked to favorable outcomes in pain improvement, better functional status, and increased sensory conduction velocity in CTS patients, although standardized dosing recommendations are not yet established
- A combination of alpha-lipoic acid, curcumin phytosome, and B-group vitamins administered orally has shown clinical usefulness in reducing nocturnal symptoms and positive Phalen’s tests in CTS patients undergoing surgical treatment9.
- Some studies have not found a significant advantage of vitamin B6 over conservative therapy for CTS, indicating that its efficacy may not be conclusive
- Untreated Carpal Tunnel Syndrome can lead to serious long-term complications, emphasizing the need for prompt management.

Symptoms related to carpal tunnel syndrome
Carpal tunnel syndrome is characterized by symptoms that are typically experienced in the hand and wrist due to compression of the median nerve within the carpal tunnel. Individuals may notice the following signs:
- Numbness: A common symptom where individuals feel a lack of sensation in their fingers, particularly the thumb, index, middle, and part of the ring fingers.
- Tingling/Pins and Needles: Frequently described as an uncomfortable “pins and needles” sensation in the hand, akin to the feeling one gets when a limb falls asleep.
- Pain: A person may experience pain ranging from mild to severe in the hand and wrist that can extend to the forearm and shoulder.
- Weakness: One might struggle with everyday tasks due to a weakened grip or difficulty in holding objects, stemming from the loss of strength in the hand.
- Nighttime Symptoms: Symptoms often worsen at night, causing discomfort and disturbing sleep.
These symptoms tend to develop gradually and can come and go initially. Over time, without treatment, they may become constant. Some individuals may find relief by shaking their hands or changing positions, but this typically becomes less effective as the condition progresses.
For an accurate diagnosis and to distinguish the symptoms from those of related conditions, please consult a healthcare professional. Individuals presenting these symptoms should seek evaluation and treatment to help prevent long-term damage and improve their quality of life.
Medical conditions commonly associated with carpal tunnel syndrome
Carpal tunnel syndrome can be associated with several medical conditions such as diabetes, rheumatoid arthritis, thyroid dysfunction, and obesity.
Chronic conditions, which persist over long periods, can have a multifaceted relationship with CTS). CTS itself can become a chronic issue when untreated and is frequently associated with various health concerns.
Hypothyroidism. Thyroid disease is a known cause of carpal tunnel syndrome (CTS), but patients with CTS symptoms are not typically screened for thyroid disease.
Patients with undiagnosed hypothyroidism may present with carpal tunnel syndrome (CTS) symptoms. It is becoming increasingly recognized that addressing the underlying thyroid condition can effectively treat CTS and potentially avoid surgery. Untreated hypothyroidism may reduce the effectiveness of surgical management for CTS.
Diabetes, a state characterized by elevated blood sugar levels, can lead to systemic complications affecting the nervous system, with peripheral neuropathy often presenting symptoms similar to CTS. Management of diabetes is crucial to prevent the progression of such complications.
In individuals with autoimmune disorders, the body’s immune response can mistakenly target its tissues, potentially causing inflammation in the carpal tunnel. This underscores the importance of vigilant disease management in autoimmune conditions.
Carpal tunnel syndrome and alcohol
- Substance Use and CTS Prevalence
- Workers with definite CTS showed a higher history of alcohol abuse and a lower current use of alcohol compared to those without CTS. Tobacco and caffeine use were also associated with an increased risk of CTS, with caffeine use posing the highest risk when used alone or with tobacco.
- Gender-Specific Predictors:
- In female workers, smoking and caffeine use were significant predictors for CTS, while in male workers, a history of alcohol abuse and current beer consumption were predictors1.
- Occupational Risk and Substance Use:
- The prevalence of CTS symptoms and median nerve slowing in specific job categories correlated directly with current tobacco use, suggesting an occupational risk factor influenced by substance use
The research indicates that the use of legal substances such as tobacco, caffeine, and alcohol may influence the risk of developing Carpal Tunnel Syndrome. While tobacco and caffeine use are generally associated with an increased risk, a history of alcohol abuse is particularly relevant for male workers. However, these factors alone explain only a small portion of the total risk, suggesting that other occupational and individual factors also play a significant role in the development of CTS.
Heart disease may also indirectly increase the risk of developing CTS due to associated vascular conditions.
Pregnancy often results in fluid retention, leading to increased pressure within the carpal tunnel and transient CTS. Moreover, obesity is a recognized risk factor for CTS, likely due to increased pressure within the carpal tunnel and systemic inflammation.
Future studies should examine the impact of visceral and total body fat on CTS.
Anemia, a reduction in red blood cells, can predispose individuals to developing CTS due to related physiological stress. Few studies3 found that Hb and ferritin levels were lower in patients with CTS.
In the conservative therapy of CTS, vitamins, notably vitamin B6, can play a role in symptom relief. While the effectiveness of vitamin B6 is debated, monitoring for symptom changes during its usage is advised, especially when high doses are consumed.
Comprehending these interconnected health conditions helps shape a holistic approach to CTS management, emphasizing the importance of addressing the broader health spectrum in chronic condition care.
Can Vitamin Deficiency Causes Carpal Tunnel Syndrome?
What Vitamin Deficiency Causes Carpal Tunnel
Vitamin D deficiency and carpal tunnel syndrome
Vitamin D deficiency is related to CTS. These studies found that there were no reported complications following vitamin D administration in CTS patients. Previous studies have reported complications from accidental overdoses, but the usual therapeutic dose of vitamin D did not noticeably increase adverse events. Therefore, oral vitamin D administration with the appropriate dose is considered safe for CTS patients.
Although limited evidence suggests that at least 12 weeks of vitamin D supplementation can improve pain outcomes and functionality in mild-moderate CTS cases, further research is needed before establishing standardized dosages or durations for treatment. Monitoring serum levels while prescribing an appropriate dose as an additional treatment option is recommended based on current evidence available.
Certain deficiencies such as B6 can exacerbate its symptoms. Bitamins B6 , and B12 play crucial roles in nerve health and function. Both vitamins are essential in maintaining proper nerve function and reducing inflammation that could contribute to the compression of the median nerve, which is characteristic of CTS.
What is the best vitamin for carpal tunnel syndrome?
Vitamin B6 is a vital cofactor needed for neuronal protein synthesis.
When considering vitamins and supplements for the management of carpal tunnel syndrome (CTS), two B vitamins, specifically vitamin B6 (pyridoxine) and vitamin B12 (cobalamin), are often mentioned for their potential benefits.
Vitamin B6 is believed to reduce symptoms due to its role in nerve health.
How Much Vitamin B6 for Carpal Tunnel?
Studies show improvement in CTS symptoms with daily doses of pyridoxine ranging from 50 to 300 mg over 12 weeks4.
Determining vitamin B6 levels in the lab can play a crucial role in making informed decisions about surgery.
It’s important to stay within the safe upper limit to avoid toxicity which can exacerbate neurological symptoms.
Consider stopping the pyridoxine if there has been no apparent response to it
after 12 weeks
In contrast, vitamin B12 is essential for maintaining the sheath that surrounds and protects nerves. Lack of B12 can lead to nerve damage, making proper supplementation vital for individuals at risk of deficiency, which can contribute to CTS.
Apart from these two, other B vitamins, such as thiamine (B1), riboflavin (B2), niacin (B3), pantothenic acid (B5), biotin (B7), folate (B9), and folic acid, also support nerve function and overall health.
Consideration should be given to natural medicines and food sources rich in these nutrients for a holistic approach. Antioxidants found in B vitamins can counteract oxidative stress, which is implicated in the exacerbation of CTS.
Proper dosage and adherence to the recommended guidelines play a crucial role in the effectiveness and safety of using vitamins and supplements for carpal tunnel syndrome.
Can carpal tunnel syndrome be reversed naturally?
The primary treatment approach for mild symptoms of carpal tunnel syndrome (CTS) involves conservative therapy, with wrist splinting being the initial preference. Wrist splints are typically worn at night to maintain a neutral wrist position. Patients should undergo a follow-up evaluation within 1 to 2 months, and if their symptoms show improvement, they should continue with splinting. However, if improvement is lacking, combining splinting with other therapeutic approaches should be considered. Referral to a specialized hand therapist may be beneficial as they can provide techniques such as carpal bone mobilization, nerve- and tendon-gliding exercises, and ultrasound therapy.
Natural ways to improve carpal tunnel syndrome often include ensuring adequate intake of these vitamins either through diet or supplementation.
DMSO should be added to the daily routine ( internal and organic cream-based containing anti-inflammatory herbs and DMSO). However, individuals should consult a healthcare provider before starting any new vitamin regimen, as it’s essential to tailor the approach to their specific health needs and conditions associated with CTS. It is also crucial to note that while addressing vitamin deficiencies may help manage CTS symptoms, they are not a standalone cure and should be part of a comprehensive treatment plan.
Which vitamin is most effective in managing symptoms of carpal tunnel syndrome, B6 or B12?
When considering the management of carpal tunnel syndrome (CTS), research indicates that vitamin B6 plays a more significant role compared to vitamin B12.
Proper dosage and effectiveness can vary based on individual conditions and should be determined by a healthcare provider.
Diet And Nutrition
Proper nutrition can play a significant role in managing and potentially improving Carpal Tunnel Syndrome (CTS). Including specific vitamins and nutrients in one’s diet might help alleviate symptoms associated with CTS.
| Food | Serving Size | Vitamin B6 Content (mg) |
|---|---|---|
| Chicken breast | 100g | 0.51 |
| Turkey breast | 100g | 0.75 |
| Tuna (yellowfin, cooked) | 100g | 0.97 |
| Salmon (cooked) | 100g | 0.55 |
| Beef (lean, cooked) | 100g | 0.47 |
| Pork loin (cooked) | 100g | 0.74 |
| Potatoes (baked) | 1 medium | 0.70 |
| Cabbage raw | 100g | 0.160 |
| Avocado | 1 medium | 0.42 |
| Apples Red Delicious | 1 medium | 0.03 |
| Banana | 100g | 0.51 |
| Pecans | 100g | 0.18 |
| Chickpeas (cooked) | 1 cup | 1.10 |
| Lentils (cooked) | 1 cup | 0.68 |
| Oatmeal (cooked) | 1 cup | 0.46 |
These values are approximate and can vary depending on factors like cooking methods and varieties of the foods.
- This study showed a fixed association of ALA (alpha-lipoic acid) 600 mg/die and y -linolenic acid GLA (gamma-linolenic acid) 360 mg/die is beneficial in managing symptoms and the progression of a certain condition. It can be considered as an pplements for controlling symptoms and promoting better outcomes.
- The inclusion of omega-3 fatty acids is another strategic dietary approach. Omega-3s, found in foods like fatty fish, flaxseed, and walnuts, are known for their anti-inflammatory properties, which could be beneficial in reducing CTS symptoms.
- Turmeric, a spice renowned for its anti-inflammatory effects, can also be incorporated into the diet. It may help in decreasing inflammation and pain related to CTS.
- A well-rounded diet inclusive of proteins, fruits, and vegetables supports overall health and can indirectly aid in managing conditions like CTS. Maintaining healthy nutrition not only benefits CTS but can contribute to better systemic health, potentially reducing the risk of related health conditions.
Long-term effects of untreated carpal tunnel syndrome
What happens if carpal tunnel syndrome is left untreated
Carpal tunnel syndrome (CTS) can lead to permanent damage to the median nerve, resulting in long-term impairment and disability. This condition can cause muscle weakness and atrophy, particularly at the base of the thumb, which can affect d. Chronic wrist and hand pain is common in CTS patients and may progress to complex regional pain syndrome.
One of the most frequent complications of carpal surgery is the development of a neuroma in the palmar cutaneous branch of the median nerve. Other potential complications include hypertrophic scars, joint stiffness, abnormal sensations (dysesthesias), and incomplete resolution of symptoms after surgery.
Conclusion
In the management of carpal tunnel syndrome (CTS), vitamins B6, B12, D play a substantial role. Evidence suggests that vitamins B6 and D, Alpha-lipoic acid (ALA), and GLA can provide symptomatic relief for some individuals dealing with CTS, although its efficacy varies from person to person. Patients considering vitamin B6 supplementation should adhere to the recommended dietary allowances to avoid the possibility of neuropathy due to excessive intake.
Natural methods, in addition to vitamin supplementation, may support the alleviation of CTS symptoms. These include ergonomic adjustments, wrist splints, and exercises specifically designed to reduce nerve pressure.
- Deveci Ş, Matur Z. Does the severity of carpal tunnel syndrome symptoms vary due to vitamin and mineral deficiencies and anemia? Neurol Sci Neurophysiol 2023;40:215‑220. ↩︎
- https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC6486195/pdf/CD003219.pdf ↩︎
- Deveci Ş, Matur Z. Does the severity of carpal
tunnel syndrome symptoms vary due to vitamin and mineral deficiencies
and anemia? Neurol Sci Neurophysiol 2023;40:215‑220. ↩︎ - Elaine Aufiero, M.D., Todd P. Stitik, M.D., Patrick M. Foye, M.D., and
Boqing Chen, M.D., Ph.D. Pyridoxine Hydrochloride Treatment of Carpal Tunnel
Syndrome: A Reviewdoi: 10.1301/nr.2004.mar.96 –104 ↩︎